top of page
Search
All Posts


5G NR PDCP & SDAP Layers
1. Introduction 5G NR fundamentally redesigned the user-plane architecture by introducing SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol) above PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol). LTE used a bearer-based QoS model. 5G uses a flow-based QoS model. This single architectural shift explains: Why SDAP was introduced Why PDCP evolved Why 5G scales better than LTE How URLLC, slicing, and dual connectivity are supported This article provides: Deep architectural explanation LTE vs 5G com

Venkateshu Kamarthi
1 day ago10 min read


Massive MIMO in 5G
1. Introduction The exponential growth in mobile data traffic, driven by 4K/8K video, cloud gaming, AR/VR, industrial IoT, and private 5G networks, has forced wireless systems to evolve beyond traditional antenna systems. One of the most transformative technologies enabling 5G performance is Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output). Unlike conventional MIMO (2x2, 4x4, 8x8), Massive MIMO scales antenna elements to tens or even hundreds at the base station, enabling spatia

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Feb 2111 min read


Power Control in 5G NR
1. Introduction Power control is one of the least visible but most influential mechanisms in cellular radio systems. In 5G NR, it directly impacts: Uplink throughput and latency Cell-edge user experience Inter-cell interference UE battery life Massive MIMO beam efficiency Network energy consumption (Green RAN goals) Unlike LTE, 5G NR operates with: Very wide bandwidths Beam-based transmission Dynamic TDD Cloud-native and O-RAN architectures As a result, power control in 5G NR

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Feb 814 min read


RLC Protocol in 5G NR
1. Introduction: Why RLC Still Matters in 5G NR When discussions around 5G performance arise, attention usually gravitates toward massive MIMO, beamforming, or spectrum efficiency. Yet, in real networks, user experience often degrades due to issues far removed from PHY or antennas. One of the most common root causes lies in the Radio Link Control (RLC) layer. In 5G NR, RLC sits between PDCP and MAC, just like LTE. But assuming it is “unchanged from LTE” is a mistake. While t

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Feb 114 min read

5G NR MAC DL/UL Scheduling Algorithms
1. Introduction Medium Access Control (MAC) scheduling is one of the most critical real-time functions in a 5G NR gNB. It directly determines throughput, latency, fairness, spectral efficiency, and QoS compliance. Unlike LTE, 5G MAC scheduling operates in a much more complex design space due to: Flexible numerology (multiple SCS) Mini-slots and slot aggregation Beam-based transmissions Massive MIMO QoS flows (5QI-driven scheduling) URLLC pre-emption and puncturing Dynamic TDD

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Jan 2316 min read


LDPC Coding in 5G NR
1. Introduction Channel coding is one of the most fundamental building blocks of the 5G NR physical layer. It directly determines: Block Error Rate (BLER) Throughput at high MCS Latency predictability UE power consumption Hardware scalability in gNB and UE Unlike LTE, which relied almost exclusively on Turbo codes, 5G NR deliberately replaced Turbo codes with Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes for data channels and Polar codes for control channels. LDPC Coding Chain in 5

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Jan 159 min read


Agentic AI in 5G RAN
1. Introduction Modern 5G radio access networks have reached a level of complexity where traditional automation approaches are no longer sufficient. While machine learning has been widely adopted in telecom analytics, most deployed solutions still behave as passive systems: they ingest data, run inference, and output a score, label, or alert. In practice, experienced RAN engineers do not work this way. They observe symptoms, form hypotheses, validate those hypotheses by check

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Dec 19, 202510 min read


Private 5G Wireless Networks
Private 5G (also referred to as Non-Public Networks — NPNs) is the deployment of 5G technologies for the exclusive use of an organization, campus, industrial site, port or stadium. Unlike public/macrocell 5G, private 5G is designed to deliver dedicated capacity, stronger security controls, low and deterministic latency, and granular service control for vertical-specific applications (robotics, automation, AR/VR, mission-critical communications). 1. What is Private 5G What it

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Dec 12, 202510 min read


The Future of Wireless Communication Unveiled: Wireless Evolution Trends
Wireless communication has undergone significant transformations over the past few decades. From the early days of analog signals to the sophisticated digital networks of today, the technology continues to evolve rapidly. As professionals and engineers working with LTE, 5G, 6G, and O-RAN technologies, understanding these changes is crucial. This article explores the wireless evolution trends shaping the industry and offers insights into what lies ahead. Understanding Wireless

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Dec 9, 20254 min read


The Role of FFT Applications in OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) has become a cornerstone technology in modern wireless communication systems such as LTE, 5G, and emerging 6G networks. At the heart of OFDM’s efficiency and robustness lie two fundamental mathematical tools: the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and its inverse (IFFT). Understanding how these transforms operate within OFDM is essential for professionals working with wireless technologies. Understanding FFT Applications in OFDM FFT
Venkateshu
Dec 8, 20253 min read


Cloud & NFV(Network Function Virtualization) for 5G Networks
1.Introduction Cloud and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) for 5G networks represent a fundamental shift in how telecommunication networks are designed and managed. NFV decouples network functions from specialized hardware, allowing them to run as software on standard cloud infrastructure. This virtualization enables 5G networks to be more flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient by leveraging cloud-native principles and automation. It allows operators to dynamically alloca

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Dec 6, 20259 min read


Exploring the 5G Quality of Service Framework
The evolution of wireless communication has brought us to the era of 5G, a technology promising unprecedented speed, low latency, and massive connectivity. However, delivering these benefits consistently requires a robust system to manage network resources effectively. This is where the 5G Quality of Service (QoS) framework plays a critical role. It ensures that different types of traffic receive appropriate treatment based on their requirements, enabling seamless user experi
Venkateshu
Dec 1, 20255 min read


RRC_INACTIVE State in 5G NR
1. Introduction The RRC_INACTIVE state represents a fundamental architectural innovation in 5G New Radio (NR), introduced to address critical latency and signaling overhead challenges that plagued LTE networks. In LTE, frequent transitions between RRC_IDLE and RRC_CONNECTED states created substantial network signaling load and introduced latency penalties during service resumption, particularly problematic for modern smartphone usage patterns characterized by frequent sm

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Nov 29, 202511 min read

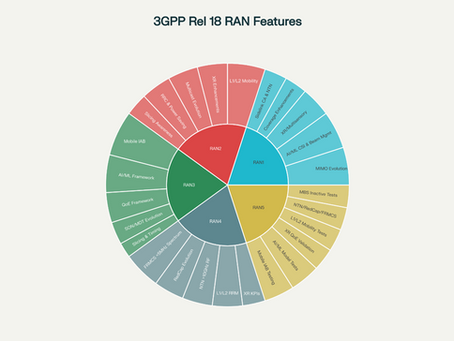
3GPP Release 18: 5G-Advanced RAN Features(RAN1 to RAN5)
Introduction 3GPP Release 18 marks the first 5G-Advanced release, focusing on AI/ML integration, extreme performance for XR/Industrial IoT, mobile IAB, enhanced positioning, and spectrum efficiency up to 71 GHz. RAN workgroups (RAN1–RAN5) deliver these through physical layer evolution, protocol optimizations, architecture updates, RF requirements, and testing frameworks. Release 18 builds on Rel-17's foundations with AI/ML for RAN optimization, centimeter-level positioning,

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Nov 28, 20259 min read


3GPP Release-17 — Features summary (RAN1 → RAN5)
1. Introduction & scope Release-17 was intended as the first major consolidation/evolution step after Rel-16: adding new vertical and architectural capability without a full redesign. Release-17 contains both PHY-centric items (RAN1) and higher layer/procedural items (RAN2, RAN3), plus RF/test requirement updates (RAN4) and conformance/OAM items (RAN5). This article focuses on the RAN WGs (RAN1–RAN5) and practical implementation details drawn from the 3GPP work items and tech

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Nov 28, 20256 min read


RAN Intelligence with xApps and rApps
1. Introduction Radio Access Networks are becoming more software-driven, disaggregated, and automation-centric. To handle the complexity of dense deployments, Massive MIMO, spectrum fragmentation, and diverse traffic profiles, operators are moving toward intelligent control loops in the RAN.This is where O-RAN Alliance’s RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) architecture—featuring rApps (non-real time, >1 second) and xApps (near-real time, 10 ms–1 s)—comes into play. These applica

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Nov 21, 202518 min read


5G gNB CU/DU/RU Split Architecture & Interfaces
1) Introduction The 5G NR gNB split architecture divides the base station into functional entities — Central Unit (CU) , Distributed Unit (DU) , and Radio Unit (RU) — to optimize deployment flexibility, scalability, and performance. This functional split enables c entralized control and distributed radio processing, allowing operators to balance latency-sensitive tasks at the edge (DU/RU) with higher-layer functions centralized (CU). The split reduces fronthaul bandwidth dem

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Nov 13, 202515 min read


O-DU ↔ O-RU Interoperability Troubleshooting (O‑RAN WG4 C/U, S & M Planes)
O-DU ↔ O-RU Interoperability Troubleshooting (O-RAN WG4 C/U, S & M Planes) focuses on identifying and resolving functional and timing mismatches between the Distributed Unit (O-DU) and Radio Unit (O-RU) across the Open Fronthaul interface defined by O-RAN Working Group 4. It provides a systematic approach to diagnosing issues in the Control/User Plane (C/U), Synchronization Plane (S), and Management Plane (M)—the three pillars of inter-vendor interoperability. The guide emph

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Nov 6, 202514 min read


AI-Driven Anomaly/Fault Detection and Management in Modern Mobile Networks
Case Study – Low throughput issue mitigation Introduction The complexity of today’s telecom networks—driven by 5G’s massive scale, distributed Radio Access Network (RAN) architectures, and virtualized infrastructure—makes operational reliability and proactive fault management both a necessity and a challenge. Static rules and threshold-based monitoring techniques, once the backbone of network assurance, are now insufficient as data velocity, volume, and variety continue to gr

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Oct 28, 202512 min read


O-RAN Radio Unit (O-RU)
Introduction O-RAN (Open Radio Access Network) represents a paradigm shift in mobile network design, transforming traditional, vendor-locked RAN systems into open, interoperable, and intelligent ecosystems. It disaggregates hardware and software components, virtualizes RAN functions, and introduces open interfaces and AI/ML-driven automation for optimization and orchestration . The O-RAN architecture decouples the traditional base station into: O-CU (Central Unit): Located

Venkateshu Kamarthi
Oct 19, 20259 min read
bottom of page
